Black Holes and related projects
Black holes exist in various places in the Universe. The University of Athens Observatory performs follow-up observations in some special cases, where multi-wavelegth campaigns aim towards understanding their nature.
OJ 287 is a BL Lac object (blazar) at redshift z = 0.306 that has shown double-peaked bursts at regular intervals of ~12 yr during the last ~40 yr. Optical photopolarimetric monitoring data from 2005 to 2009 were studied, with the aim to analyse variability patterns and statistical properties of the optical polarization light curve. A strong preferred position angle in optical polarization was found after this study. The preferred position angle can be explained by separating the jet emission into two components: an optical polarization core and chaotic jet emission. This can possibly suggest that both the double-peaked bursts and the evolution of the optical polarization position angle could be explained as a sign of resonant accretion of magnetic field lines, a 'magnetic breathing' of the disc.
Artistic impression of blazar OJ 287 and a combined X-ray (Chandra) and radio image (VLA).
The study of the binary black hole OJ287 is still undergoing and so far it gave two publications in refereed journals:
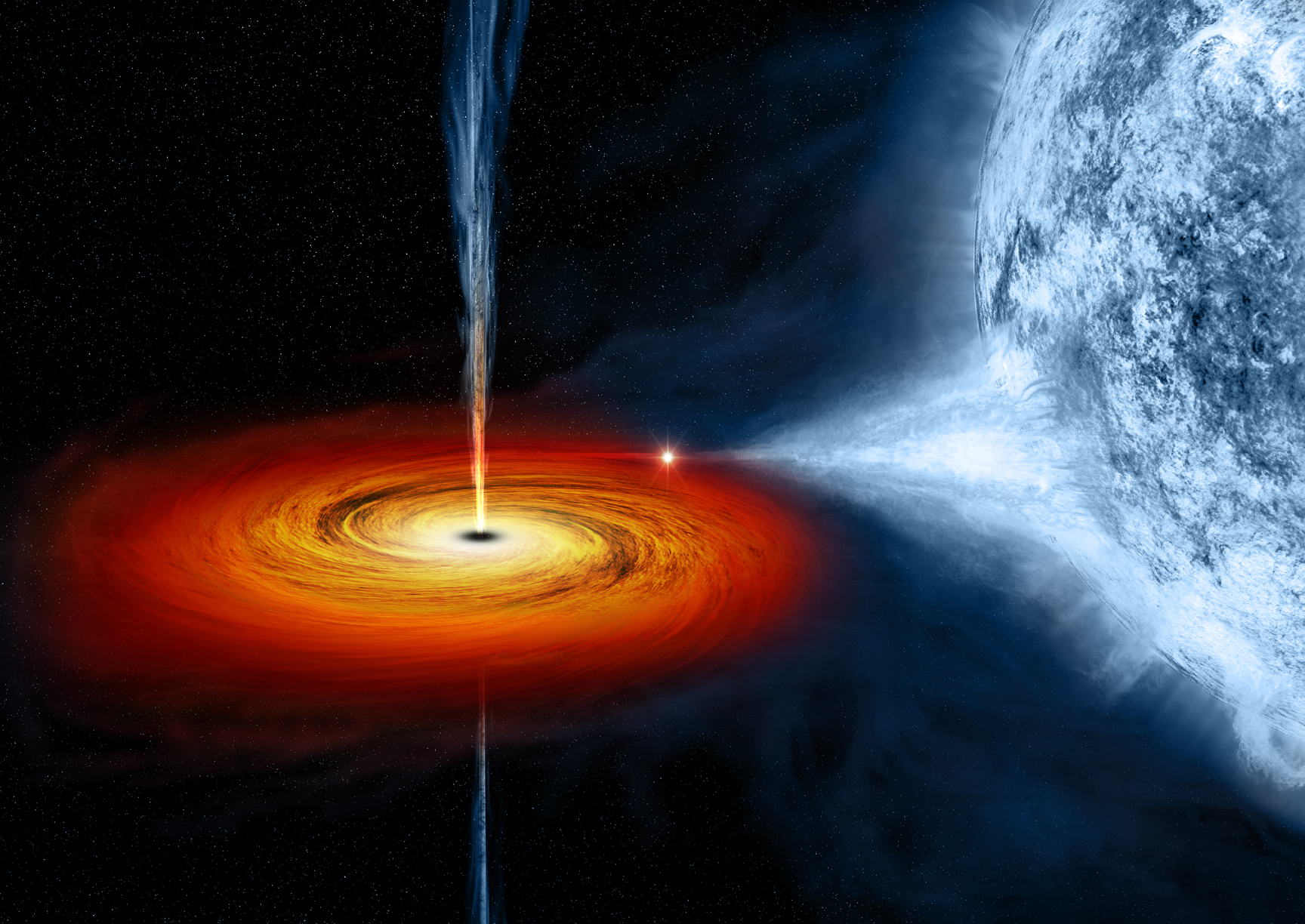
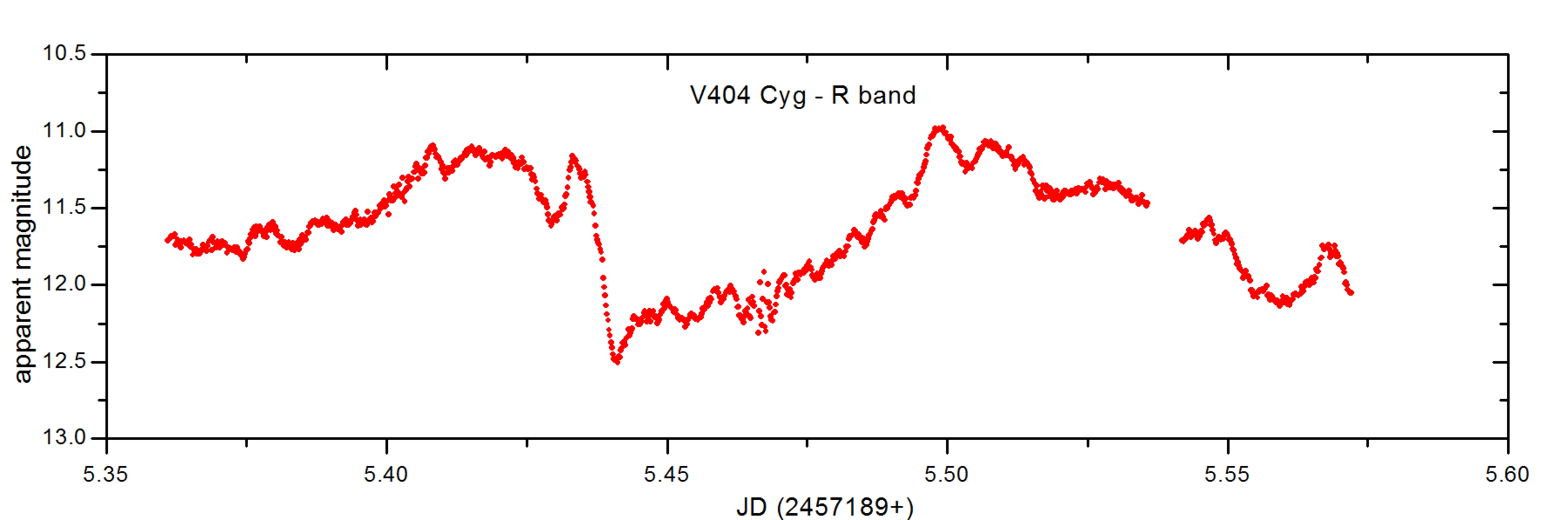
Optical Monitoring Of The Active Black Hole V404 Cyg was started on 15 June 2015, after the SWIFT trigger for a possible gamma-ray busrt. This black hole binary was followed for the next 75 nights in optical R-band, utilizing the 0.40 m f/8 robotic and remote controlled telescope at the University of Athens Observatory.
The black hole binary system V404 Cyg gave a large outburst on June 15, 2015. An artistic representation of the binary system is given at top left figure, while a sample of an active photometric behavior is shown at top right figure. Continuous monitoring of this target from the University of Athens Observatory resulted in a 75-day long photometric light curve, part of which is shown in the bottom plot.
The study of V404 Cyg resulted so far in the following announcements:
Team members
Collaboration between the University of Athens (Greece) and several other Institutes worldwide. Among them, the major collaborators are: