References
1. C. Baskakis, V. Magrioti, N. Cotton, D. Stephens, V. Constantinou-Kokotou, E. A. Dennis, G. Kokotos, J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 8027-8037.
2. A. Kalyvas, C. Baskakis, V. Magrioti, V. Constantinou-Kokotou, D. Stephens, R. Lopez-Vales, J.-Q. Lu, V. Yong, E. A. Dennis, G. Kokotos, S. David, Brain 2009, 132, 1221-1235.
3. V. Magrioti, G. Kokotos, Exp. Opin. Ther. Patents 2010, 20, 1-18.
4. G. Kokotos, Y.-H. Hsu, J. E. Burke, C. Baskakis, C. G. Kokotos, V. Magrioti, E. A. Dennis, J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3602-3610.
5. E. A. Dennis, J. Cao, Y.-H. Hsu, V. Magrioti, G. Kokotos, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130-6185.
6. V. Magrioti, A. Nikolaou, A. Smyrniotou, I. Shah, V. Constantinou-Kokotou, E. A. Dennis, G. Kokotos, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2013, 21, 5823-5829.
7. C. Dedaki, M. G. Kokotou, V. D. Mouchlis, D. Limnios, X. Lei, C. T. Mu, S. Ramanadham, V. Magrioti, E. A. Dennis, G. Kokotos. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2916?2927.
1. C. Baskakis, V. Magrioti, N. Cotton, D. Stephens, V. Constantinou-Kokotou, E. A. Dennis, G. Kokotos, J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 8027-8037.
2. A. Kalyvas, C. Baskakis, V. Magrioti, V. Constantinou-Kokotou, D. Stephens, R. Lopez-Vales, J.-Q. Lu, V. Yong, E. A. Dennis, G. Kokotos, S. David, Brain 2009, 132, 1221-1235.
3. V. Magrioti, G. Kokotos, Exp. Opin. Ther. Patents 2010, 20, 1-18.
4. G. Kokotos, Y.-H. Hsu, J. E. Burke, C. Baskakis, C. G. Kokotos, V. Magrioti, E. A. Dennis, J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3602-3610.
5. E. A. Dennis, J. Cao, Y.-H. Hsu, V. Magrioti, G. Kokotos, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130-6185.
6. V. Magrioti, A. Nikolaou, A. Smyrniotou, I. Shah, V. Constantinou-Kokotou, E. A. Dennis, G. Kokotos, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2013, 21, 5823-5829.
7. C. Dedaki, M. G. Kokotou, V. D. Mouchlis, D. Limnios, X. Lei, C. T. Mu, S. Ramanadham, V. Magrioti, E. A. Dennis, G. Kokotos. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2916?2927.
The phospholipase A2 (PLA2) superfamily consists of many different groups of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of the ester bond at the sn-2 position of various phospholipids. The products of the hydrolysis are a free fatty acid and a lysophospholipid, which both may generate second messengers that play important physiological roles. The PLA2 superfamily currently contains 15 separate, identifiable groups and various subgroups. The three predominant types of PLA2 found in human tissues are the cytosolic (such as the GIVA cPLA2), the secreted (such as the GIIA and GV sPLA2), and the calcium-independent (such as the GVIA iPLA2) enzymes. GIVA cPLA2 is generally considered a pro-inflammatory enzyme which is the rate-limiting provider of arachidonic acid and lysophospholipids. In many cases, the activity of secreted PLA2 has been shown to be dependent on or linked to the activity of GIVA cPLA2.
The calcium-independent Group VIA iPLA2 (GVIA iPLA2), typically referred to in the literature as iPLA2, is actually a group of cytosolic enzymes ranging from 85 to 88 kDa and expressed as several distinct splice variants of the same gene. GVIA iPLA2 has long been proposed as a homeostatic enzyme involved in basal metabolism within the cell. However, a number of studies suggest that GVIA iPLA2 also plays important roles in numerous cell types, although they may differ from cell to cell. Recent review articles discuss the role of GVIA iPLA2 in signaling and pathological conditions (for example, cancer and ischemia).
The GVIA iPLA2 enzyme contains a consensus lipase motif, Gly-Thr-Ser*-Thr-Gly, with the catalytic serine confirmed by site-directed mutagenesis. Both of the intracellular enzymes GIVA cPLA2and GVIA iPLA2 share the same catalytic mechanism utilizing a serine residue as the nucleophile. The various inhibitor classes of both enzymes are summarized in a review article, while another recent review article analyzes all the PLA2 enzymes, their roles and activities and their inhibitors.
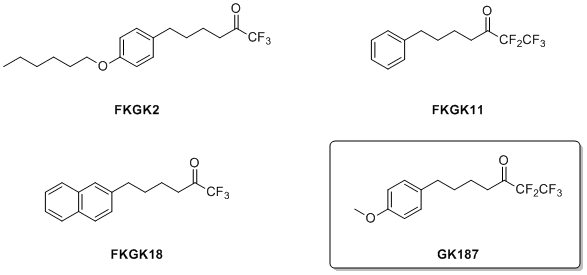
The development of selective inhibitors for the three main human PLA2 enzymes is an important goal, and we have screened a variety of polyfluoro ketones for their activity on GIVA cPLA2, GVIA iPLA2 and GV sPLA2. We have found that 1,1,1,2,2-pentafluoro-7-phenylheptan-3-one (FKGK11) is a selective inhibitor of GVIA iPLA2. FKGK11 was successfully used to study the role of this enzyme in neurological disorders such as the peripheral nerve injury and multiple sclerosis. We successfully demonstrated that FKGK11 causes a beneficial therapeutic effect in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, the animal model of multiple sclerosis. This indicates that GVIA iPLA2 is a novel target for the development of new therapies for multiple sclerosis. The recently emerged important pharmaceutical significance of GVIA iPLA2 and the lack of potent and selective GVIA iPLA2 inhibitors, prompted us to extend our studies towards the discovery of such inhibitors. We have reported various fluoroketones and the study of their selectivity on the three main human phospholipases A2. In 2010, FKGK18 [1,1,1-Trifluoro-6-(naphthalen-2-yl)hexan-2-one] was the most potent inhibitor of GVIA iPLA2 (XI(50) 0.0002) ever reported.
In the most recent article, we presented 1,1,1,2,2-pentafluoro-7-(4-methoxyphenyl)heptan-3-one (GK187) that is the most potent and selective GVIA iPLA2 inhibitor ever reported with a XI(50) value of 0.0001, and with no significant inhibition against GIVA cPLA2 or GV sPLA2.
The calcium-independent Group VIA iPLA2 (GVIA iPLA2), typically referred to in the literature as iPLA2, is actually a group of cytosolic enzymes ranging from 85 to 88 kDa and expressed as several distinct splice variants of the same gene. GVIA iPLA2 has long been proposed as a homeostatic enzyme involved in basal metabolism within the cell. However, a number of studies suggest that GVIA iPLA2 also plays important roles in numerous cell types, although they may differ from cell to cell. Recent review articles discuss the role of GVIA iPLA2 in signaling and pathological conditions (for example, cancer and ischemia).
The GVIA iPLA2 enzyme contains a consensus lipase motif, Gly-Thr-Ser*-Thr-Gly, with the catalytic serine confirmed by site-directed mutagenesis. Both of the intracellular enzymes GIVA cPLA2and GVIA iPLA2 share the same catalytic mechanism utilizing a serine residue as the nucleophile. The various inhibitor classes of both enzymes are summarized in a review article, while another recent review article analyzes all the PLA2 enzymes, their roles and activities and their inhibitors.
The development of selective inhibitors for the three main human PLA2 enzymes is an important goal, and we have screened a variety of polyfluoro ketones for their activity on GIVA cPLA2, GVIA iPLA2 and GV sPLA2. We have found that 1,1,1,2,2-pentafluoro-7-phenylheptan-3-one (FKGK11) is a selective inhibitor of GVIA iPLA2. FKGK11 was successfully used to study the role of this enzyme in neurological disorders such as the peripheral nerve injury and multiple sclerosis. We successfully demonstrated that FKGK11 causes a beneficial therapeutic effect in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, the animal model of multiple sclerosis. This indicates that GVIA iPLA2 is a novel target for the development of new therapies for multiple sclerosis. The recently emerged important pharmaceutical significance of GVIA iPLA2 and the lack of potent and selective GVIA iPLA2 inhibitors, prompted us to extend our studies towards the discovery of such inhibitors. We have reported various fluoroketones and the study of their selectivity on the three main human phospholipases A2. In 2010, FKGK18 [1,1,1-Trifluoro-6-(naphthalen-2-yl)hexan-2-one] was the most potent inhibitor of GVIA iPLA2 (XI(50) 0.0002) ever reported.
In the most recent article, we presented 1,1,1,2,2-pentafluoro-7-(4-methoxyphenyl)heptan-3-one (GK187) that is the most potent and selective GVIA iPLA2 inhibitor ever reported with a XI(50) value of 0.0001, and with no significant inhibition against GIVA cPLA2 or GV sPLA2.
Phospholipase A2 Inhibitors - iPLA2 Inhibitors
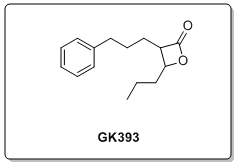
Furthermore, we have recently reported a new class of potent and selective GVIA PLA2 inhibitors that contain the â-lactone ring.