Organocatalysis
Organocatalysis has emerged as one of the most modern and rapidly growing area of organic chemistry. We have developed a variety of organocatalysts (proline derivatives, proline-modified dendrimers, proline-modified carbon nanotubes, thioureas based on natural amino acids) and we have used them for the enantioselective synthesis on known drugs.
“Functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes in a aldol reaction” D. Chronopoulos, C. G. Kokotos, N. Karousis, G. Kokotos, N. Tagmatarchis Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2750-2757.
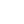
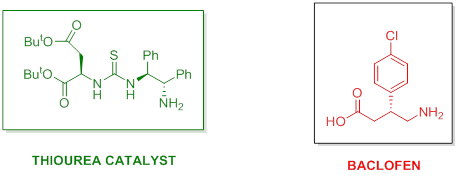
“Primary amine-thioureas with improved catalytic properties for “difficult” Michael reactions: Efficient organocatalytic syntheses of (S)-baclofen, (R)-baclofen and (S)-phenibut” M. Tsakos, C. G. Kokotos, G. Kokotos Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 740–746.
“A tripeptide-like prolinamide-thiourea as an aldol reaction catalyst.” S. Fotaras, C. G. Kokotos, G. Kokotos Org. Biomol.Chem., 2012, 10, 5613-5619.
“Primary amine-thioureas based on tert-butyl esters of natural amino acids as organocatalysts for the Michael reaction”. Kokotos, C. G.; Kokotos, G., Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 1355-1362.
“Proline-modified poly(propyleneimine) dendrimers as catalysts for asymmetric aldol reactions”. Bellis, E.; Kokotos, G., J. Mol. Cat. A: Chemical 2005, 241, 166-174.
Use of enzymes in Organic Synthesis
The application of biocatalysts in organic synthesis may offer excellent alternatives to chemical methods, because enzymes: (i) carry out highly chemo- and region-selective transformations, (ii) usually operate at neutral pH values, and (iii) combine a high selectivity for the reactions they catalyze and the structure they recognize with a broad substrate tolerance. We have studied the application of various enzymes (for example, BS2 esterase from Bacillus subtilis, CAL-A lipase from Candida Antarctica) in organic synthesis, for example for selective removal of protecting groups.
“Biocatalyzed regio- and chemoselective ester cleavage: Synthesis of bioactive molecules” E. Barbayianni, G. Kokotos ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 592–608.
“Enzymatic removal of carboxyl protecting groups. III. Fast removal of allyl and chloroethyl esters by Bacillus subtilis esterase (BS2)”. Fotakopoulou, I.; Barbayianni, E.; Constantinou-Kokotou, V.; Bornscheuer, U. T.; Kokotos, G., J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 782-786.
“Enzymatic removal of carboxyl protecting groups. 1. Cleavage of the tert-butyl moiety”. Schmidt, M.; Barbayianni, E.; Fotakopoulou, I.; Hohne, M.; Constantinou-Kokotou, V.; Bornscheuer, U. T.; Kokotos, G. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 3737-3740.