Publications
Table of Contents (TOC)
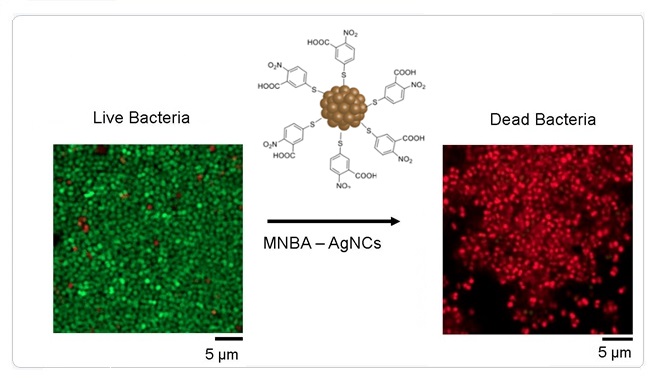
Bactericidal Effect of 5-Mercapto-2-nitrobenzoic Acid-Coated Silver Nanoclusters Against Multidrug-Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12(25), 27994–28003. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c06163
Abstract
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is among the most multidrug-resistant bacteria in circulation today, and new treatments are urgently needed. In this work, we demonstrate the ability of 5-mercapto-2-nitrobenzoic acid-coated silver nanoclusters (MNBA-AgNCs) to kill strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Using an in vitro bactericidal assay, MNBA-AgNCs were found to show significantly higher anti-gonococcal bioactivity than the antibiotics ceftriaxone and azithromycin and silver nitrate.These nanoclusters were effective against both planktonic bacteria and a gonococcal infection of human cell cultures in vitro. Treatment of human cells in vitro with MNBA-AgNCs did not induce significant release of lactate dehydrogenase, suggesting minimal cytotoxicity to eukaryotic cells. Our results suggest that MNBA-AgNCs hold great potential for topical treatment of localized gonorrhoea.
For citation:
Lucio, M. I.; Kyriazi, M. E.; Hamilton, J.; Batista, D.; Sheppard, A.; Sams-Dodd, E.; Humbert, M. V.; Hussain, I.; Christodoulides, M.; Kanaras, A. G.
"Bactericidal Effect of 5-Mercapto-2-nitrobenzoic Acid-Coated Silver Nanoclusters Against Multidrug-Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae"
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12(25), 27994–28003. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c06163