Publications
Table of Contents (TOC)
Light-Induced Reversible DNA Ligation of Gold Nanoparticle Superlattices
ACS Nano 2019, 13(5), 5771–5777. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01294
Abstract
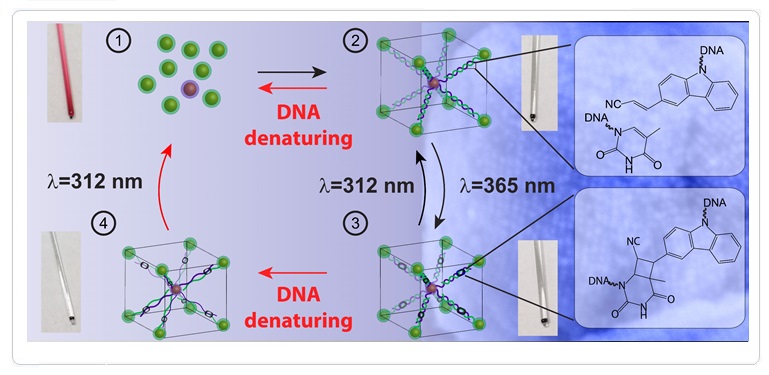
DNA-mediated self-assembly of nanoparticles has been of great interest because it enables access to nanoparticle superstructures that cannot be synthesized otherwise. However, the programmability of higher-order nanoparticle structures can be easily lost under DNA-denaturing conditions. Here, we demonstrate that light can be employed as an external stimulus to control the stability of nanoparticle superlattices (SLs) via the promotion of a reversible photoligation of DNA in SLs.
The oligonucleotides attached to the nanoparticles are encoded to ligate using 365 nm light, effectively locking the SLs and rendering them stable under DNA-denaturing conditions. The reversible process of unlocking these structures is possible by irradiation with light at 315 nm, recovering the structures to their natural state. Our work inspires a new research direction towards post-assembly manipulation of nanoparticle superstructures using external stimuli to enrich the library of new material forms and their applications in different media and environments.
For citation:
De Fazio, A. F.; El-Sagheer, A. H.; Kahn, J. S.; Nandhakumar, I.; Burton, M. R.; Brown, T.; Muskens, O. L.; Gang, O.; Kanaras, A. G.
"Light-Induced Reversible DNA Ligation of Gold Nanoparticle Superlattices"
ACS Nano 2019, 13(5), 5771–5777. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01294