Publications
Table of Contents (TOC)
Biosurfactant Coated Silver and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Enhanced Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Adhesive Properties
Journal of Hazardous Materials 2019, 364, 441–448. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.049
Abstract
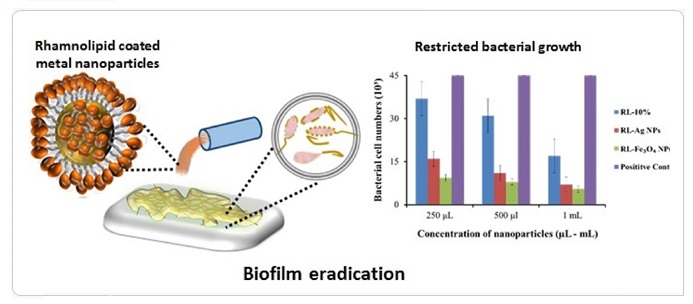
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus are among the hazardous biofilm-forming bacteria ubiquitous in industrial and clinical wastes. Serious efforts are required to develop effective strategies to control surface-growing antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacterial communities, which are emerging as a global health issue. Blocking hazardous biofilms is a useful aspect of biosurfactant-coated nanoparticles (NPs). In this regard, we report a facile method for the synthesis of rhamnolipid (RL) coated silver (Ag) and iron oxide (Fe₃O₄) NPs and propose the mechanism of their synergistic antibacterial and anti-adhesive properties against biofilms formed by P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. These NPs demonstrated excellent anti-biofilm activity not only during biofilm formation but also on pre-formed biofilms. Mechanistically, RL coated silver (35 nm) and Fe₃O₄ NPs (48 nm) generate reactive oxygen species, which contribute to the antimicrobial activity. The presence of the RL shell on the nanoparticles significantly reduces cell adhesion by modifying surface hydrophobicity, hence enhancing the anti-biofilm properties of NPs against both strains. These findings suggest that RL coated Ag and Fe₃O₄ NPs may be used as potent alternatives to reduce infection severity by inhibiting biofilm formation and possess potential biomedical applications for antibacterial coatings and wound dressings.
For citation:
Khalid, H. F.; Tehseen, B.; Sarwar, Y.; Hussain, S. Z.; Khan, W. S.; Raza, Z. A.; Bajwa, S. Z.; Kanaras, A. G.; Hussain, I.; Rehman, A.
"Biosurfactant Coated Silver and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Enhanced Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Adhesive Properties"
J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 441–448. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.049