Publications
Table of Contents (TOC)
Site-Specific Ligation of DNA-Modified Gold Nanoparticles Activated by the Restriction Enzyme StyI
Small, 2007, 3 (1), 67-70
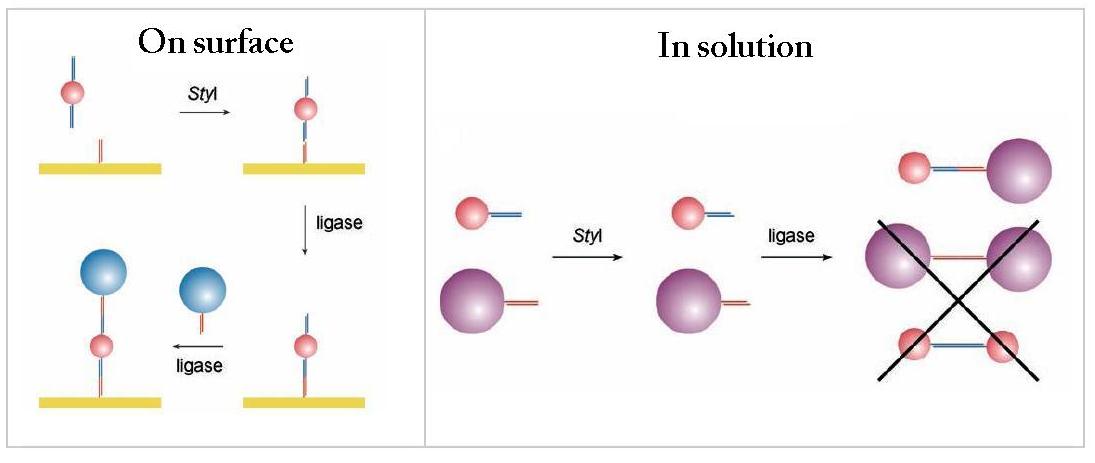
Abstract
A new method of enzymatically controlled nanoparticle assembly has been developed by using a restriction enzyme that recognizes an asymmetric DNA site. The site-selective binding of gold nanoparticles to each other and to surfaces has been demonstrated in proof-of-principle experiments.
For citations:
Kanaras, A. G.; Wang, Z.; Hussain, I.; Brust, M.; Cosstick, R.; Bates, A. D.
Site-Specific Ligation of DNA-Modified Gold Nanoparticles Activated by the Restriction Enzyme StyI
Small, 2007, 3 (1), 67-70
DOI: 10.1002/smll.200600464