Publications
Table of Contents (TOC)
Highly sensitive DNA sensor based on upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7 (23), 12422-12429. DOI: 10.1021/am507591u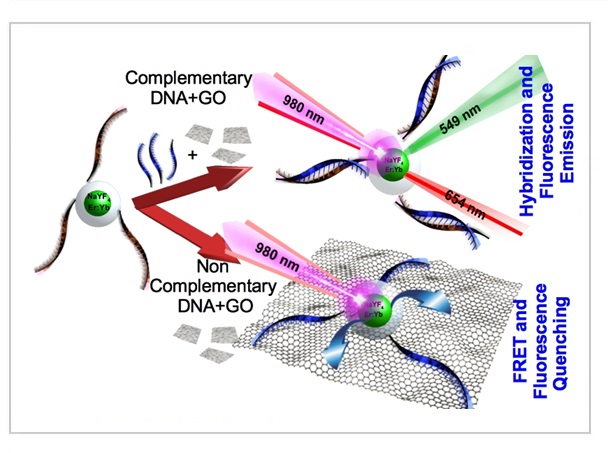
Abstract
In this work we demonstrate a DNA biosensor based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between NaYF4:Yb,Er nanoparticles and graphene oxide (GO). Monodisperse NaYF4:Yb,Er nanoparticles with a mean diameter of 29.1 ± 2.2 nm were synthesized and coated with a SiO2 shell of 11 nm, which allowed the attachment of single strands of DNA. When these DNA-functionalized NaYF4:Yb,Er@SiO2 nanoparticles were in proximity to the GO surface, the π-π stacking interaction between the nucleobases of the DNA and the sp2 carbons of the GO induced a FRET fluorescence quenching due to the overlap of the fluorescence emission of the NaYF4:Yb,Er@SiO2 and the absorption spectrum of GO. By contrast, in the presence of complementary DNA strands, hybridization leads to double-stranded DNA that does not interact with the GO surface, and thus the NaYF4:Yb,Er@SiO2 nanoparticles remain unquenched and fluorescent. The high sensitivity and specificity of this sensor introduces a new method for the detection of DNA with a detection limit of 5 pM.
For citation:
Alonso-Cristobal, P.; Vilela, P.; El-Sagheer, A. H.; Lopez-Cabarcos, E.; Brown, T.; Muskens, O. L.; Rubio-Retama, J.; Kanaras, A. G.
"Highly sensitive DNA sensor based on upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide"
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7 (23), 12422-12429. DOI: 10.1021/am507591u